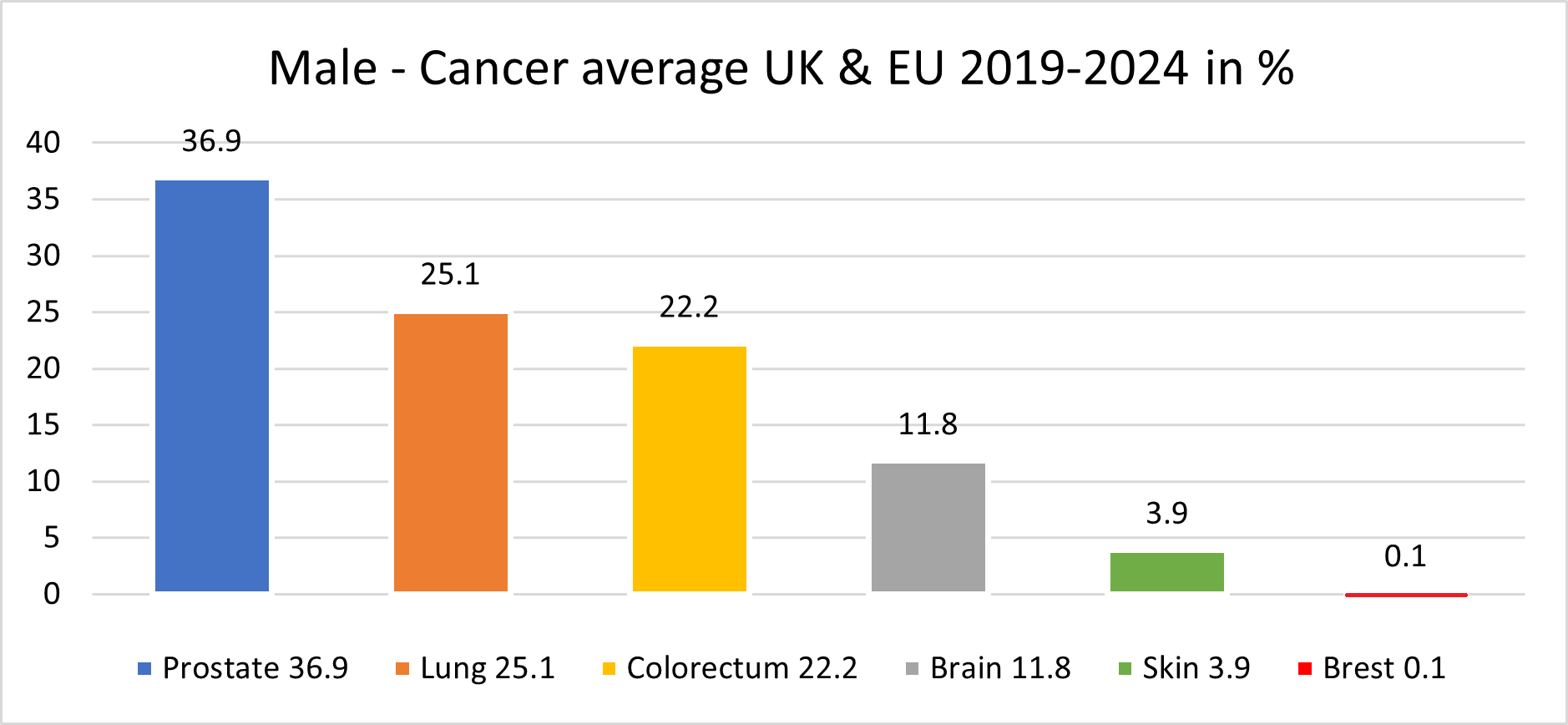
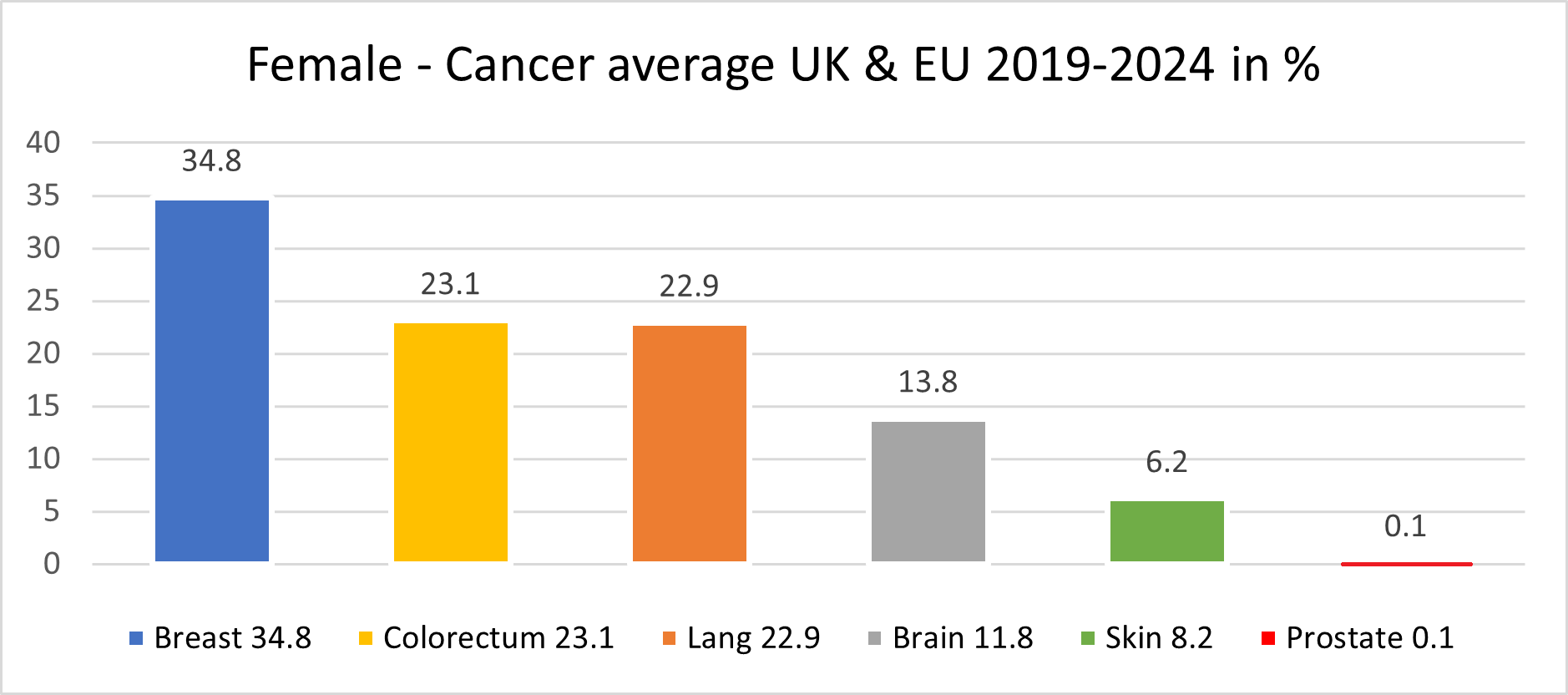
STANDARD TREATMENT OF BRAIN CANCER
Brain cancer encompasses a range of tumours originating in the brain, with glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) being the most aggressive and prevalent malignant form in adults.
There are approximately 16% of all primary brain tumours, GBM poses significant challenges due to its rapid progression and resistance to conventional treatments therefore, we highly recommend if patient has such cancer to go rather with our new method where survival time post-diagnosis is approximately 5 years, with about 24% of patients surviving beyond five years.
In Europe in the United Kingdom the incidence of GBM varies, with estimates ranging from 3.26 to 4.52 cases per 100,000 person yearly. While in the United States, there is over 14,000 new cases yearly.
The disease is slightly more common in men than in women.
Standard treatments for brain cancer in Europe and in the United Kingdom are designed to remove or destroy tumour cells while preserving neurological function. These approaches often involve a combination of surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy tailored to the individual patient's condition.
Each of these brain cancer treatment options has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of therapy depends on various factors, including the type, size, and location of the tumour, as well as the patient's overall health.
Book Your Brain Cacner Standard Treatment Here
STANDARD PROCEDURES IN EUROPE AND IN THE UNITED KINGDOM
SURGICAL PROCEDURE
Surgical intervention is typically the first basic step in treating brain tumours, especially when the tumour is accessible and operable.
A craniotomy involves removing a portion of the skull to access the brain and excise the tumour.
The goal is to remove as much of the tumour as possible while ensuring patient safety, which can alleviate symptoms and improve the effectiveness of subsequent treatments.
However, complete removal may not be feasible if the tumour is located near critical brain regions.
RADIOTHERAPY
Radiotherapy uses high-energy beams, such as X-rays or protons, to target and kill cancer cells. External beam radiation is the most common form, in which the radiation is directed at the tumour from outside the body.
This treatment can be used post-surgery to eliminate any remaining cancer cells or as a primary treatment when surgery is not an option.
Proton therapy is an advanced form of radiation that uses protons instead of X-rays. This method allows for more precise tumour targeting, minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue. It is particularly beneficial for treating tumours located near sensitive areas of the brain and is associated with fewer side effects compared to traditional radiation therapy.
CHEMOTHERAPY
Chemotherapy involves the use of drugs to destroy cancer cells.
It is often combined with surgery and radiotherapy.
Although chemotherapy can be effective, it may cause side effects such as nausea, fatigue, and an increased susceptibility to infections.
All these 3 standard brain cancer treatment options has its own advantages and limitations, and the choice of therapy depends on the type, size, and location of the tumour, as well as the patient's overall health.
NEUROENDOCRINE TUMOURS (NETs)
A neuroendocrine tumour, or NET, is a quite rare neoplasm that can develop in any body regions where the hormone-producing cells are present. Tumours that develop from the neuroendocrine cells preserve the ability to produce hormones and respond to the impulses from the autonomic nervous system. In addition to the unusual and variable clinical picture due to the hormone overproduction, NETs can develop features of malignant neoplasms, invade healthy tissues and requiring active therapy.
Pathophysiology and causes of neuroendocrine tumours
There are neuroendocrine tumours unites heterogeneous neoplasms that arise from the lungs, adrenal glands, appendix, rectum, pancreas, and other organs of the digestive tract. Their common feature is combining properties of hormone-producing cells and nerve cells. Neuroendocrine tumours are able to accept electric signals from the nervous system and discharge hormones into the bloodstream in response to such stimuli. Pathohistological of such tumours depends on the type of the progenitor cell.
Types of neuroendocrine tumours
Neuroendocrine tumours are quite rare neoplasms that arise from the specialized cells of the neuroendocrine system. The neuroendocrine system is present in many organ systems, as it controls and coordinates a number of the body’s functions. NETs are usually considered malignant neoplasms, despite many of them growing slowly and needing years to develop.
Depending on the growth speed, tendency to metastasize, and invading neighbouring organs, all NETs can be divided into benign and malignant ones. Benign or non-cancerous tumours grow slowly and manifest themselves mainly with unexplainable hormonal changes. Malignant or cancerous ones tend to spread through the organism, invade nearby organs and cause local and hormonal symptoms.
We find no links that neuroendocrine cancer hereditary nature, therefore, parents with this condition may give birth to healthy children. However, must be noted that certain hereditary conditions are associated with higher risks of NET development. Thus, in the presence of MEN-1, MEN-2, etc., attention should be paid to NET screening.
The majority of NET tumours are sporadic. This means that they are not transmitted from parents to children but arise as newly onset conditions. Nevertheless, few hereditary syndromes increase the chances of developing microcarcinoma. These are multiple endocrine neoplasia Type 1, multiple endocrine neoplasia Type 2, neurofibromatosis, von Hippel-Lindau syndrome, and tuberous sclerosis.
Neuroendocrine tumour classification depends on the localization and hormonal activity. Following these criteria the following tumour types are distinguished:
GASTROENTEROPANCREATIC
Gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumours are most often found at age 50-60 by accident (during surgical interventions for other reasons). This is connected with the absence of acute and specific clinical manifestations. Gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumours include the following subtypes:
- Appendiceal neoplasms are typically found postoperatively, during the histological examination of the removed during appendectomy tissue specimens. Appendiceal neoplasms are benign and rarely cause carcinoid syndrome (in less than 1% of cases).
- Gastric neoplasms may be associated with chronic atrophic gastritis, Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, MEN-1, or sporadic. These are usually the sporadic tumors that actively produce histamine and serotonin, causing an atypical carcinoid syndrome.
- Colorectal neoplasms are divided into small-cell and moderately differentiated carcinomas. The first ones are somewhat similar to small-cell lung cancer and require chemotherapy. The second ones resemble large-cell lung carcinoma and are successfully treated surgically.
- Pancreatic neoplasms originate from the diverse cells of pancreatic islets.
Due to the diversity of secreted hormones, the pancreatic NETs are divided into numerous subtypes:
- Insulinoma is a beta-cell neoplasm that is capable of excessive insulin secretion. This is the most widespread pancreatic NET.
- Gastrinoma typically arises in the pancreas or duodenum and is responsible for the development of Zollinger-Ellison syndrome or peptic ulcers against the background of high gastrin levels.
- VIPoma is a component of MEN-1 syndrome. VIPoma autonomously and uncontrollably synthesizes the vasoactive intestinal peptide.
- Somatostatinoma is the rarest pancreatic NET. High levels of hormone somatostatin suppress the work of the gastrointestinal tract, and the diagnosis is easily confirmed by the elevated somatostatin blood levels.
- Pancreatic polypeptide-secreting tumour is a rather common NET type, although it is not associated with any clinical syndrome. Non-specific symptoms, like abdominal pain or jaundice, may be associated with the tumor presence.
ADRENAL CANCER and PHEOCHROMOCYTOMA
Pheochromocytoma is a benign neoplasm that arises from the adrenal gland. This is a rather common condition characterized by the excessive secretion of catecholamines and is often found in young patients with arterial hypertension. On the contrary, adrenal cancer is a malignant pathology that tends to metastasize to distant body parts.
MERKEL CELL CARCINOMA
Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare skin malignant neoplasm that arises on the head, neck, or face. The condition is typically diagnosed in older people, as well as in people with weak immunity. The tumour may be superficial or may spread deeper, beyond the skin.
GENITOURINARY TRACT TUMOURS
Tumours of the genitourinary tract appear in kidneys and bladder, ovaries and cervix uteri (women), prostate, and testicles (men). Due to the weak hormonal activity, they are rarely diagnosed (except for testicular and ovarian ones).
PULMONARY TUMOURS
Pulmonary tumours comprise typical and atypical carcinoids, large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma, and small-cell lung carcinoma. The pathologies are listed in order of aggressiveness increasing and prognosis worsening. It should be noted that pulmonary and endocrine neuro cancer has the same cell of origin as small cell lung cancer.
This is paragraph text. Click it or hit the Manage Text button to change the font, color, size, format, and more. To set up site-wide paragraph and title styles, go to Site Theme.
YOUR QUESTIONS ANSWERED
Can I choose the hospital for my treatment?
Yes, you can select the hospital you would like to be during your treatment, however, keep in mind that that particular hospital must have a department and wards for the kind of profile of your medical issue. When the patients identify where they would like to have their treatment, they must have in mind the remoteness from the airports, main road and main railways in cases of any emergencies.
We’ll give our recommendation which is based on a long experience and a profound analysis of all criteria necessary for the quality of medical the patients are looking for.
How much does treatment cost?
When you book your treatment with us you will get fix figure of which you are paying just ¼ of original cost only, the balance of ¾ contributed and paid by Zdenko Kos Foundation.
Costs for hospitals are also fixed for entire year, therefore, if you are having treatment over one year, the hospital costs might changed. Once you make the payment for the hospital (eg.for one year) you have hospital free of any charges doesn't matter how many times and days per year you spent in the hospital, doesn't matter how many times you are book and discharged from the hospital.
What is the cost of your services
Depending on the duration of the medical program the cost in every hospital doesn't matter, the country may vary - but not when you are booking with us. Our prices are fixed doesn't matter what we may find once eg. surgery or treatment start. All the costs of our services are significantly lower, up to 80% (depending on treatment) that you will have to pay either through your health system in your country or when organizing the program on your own. There are several reasons for it: The hospitals provided by us have special contract agreements to have fixed rates with discounts for the entire year. There are no overstated rates. You and the hospital you will be having treatment are insured specially from unforeseen expenses eg. possible complications.
With whom will I conclude the contract?
You must book with us, and you will complete the contract with us - The Zdenko Kos Foundation. It is a contract on the organization of a medical trip and provision of services. The protocol is very clear:
[1] You have to make the booking with us online on this web site (see the page with the booking box) for the treatment you are after where we are strongly suggest to give us as much data and images of your medical condition to date that we can contact you directly with our doctors, consultants and other medical staff for the treatment you would like to have.
[2] Once booking is completed, you will receive automated mail for the payment to be made. You have to make the payment in full for the treatment you would like to have in maximum 24 hours after the booking. With making the payment you start ball rolling.
[3] Being admitted to the hospital, you will conclude a direct contract with us for the provision of medical services.
{4} Once payment made you will get direct link to the doctor and counsaltant to discuss your case face-to-face via What's Up or other such service provider available to both parties depend on your locatition.
Why should I pay you, but not the hospital?
Firstly, unlike many intermediary firms and portals, we do not take from hospitals a percentage of the medical service cost because we have contract agreement not just with hospitals but also with doctors, consultants and other medical professional in each hospital we are working with.
Secondly, we are covering ¾ of costs for your procedure not to mention that your procedure-treatment will be fully insured up to £250,000 (for one year treatment) and automatically up to £500,000 (for 2-5 years treatment). The Zdenko Kos Foundation cover the hospital insurance seperately during your treatment if there may come to unforseen complication during the treatment.
Finally, as we are registered as charity, we remain independent in choosing a medical facility and work exclusively for the benefit of the patient. Any type of payment for sending a patient to the hospital is prohibited by law, since it contradicts medical ethics.
At what point do the services become paid?
The services for the organization of treatment become paid from the moment you made your medical treatment booking online and make the payment in full. Once this done, pre-treatment consultation will take the place following the initial examination (hospitalization).
Can I contact the hospital directly?
Yes, of course, you can also contact the hospital on your own. You should choose the hospital and the attending doctor, write an email to the chief doctor with a description of your case in English, ask him/her about the possibility of undergoing treatment in the hospital and the approximate cost of staying there. If you have received the consent of the hospital and you are satisfied with the price for the hospital (please specify that it must be the price for one year doesn’t matter on number of admissions and discharges and transfer an advance payment to us on our account. Once full payment is received, we will negotiate special terms with the hospital you select on your own that they will be aware of what and how many procedures they have to have in mind and secure at any time free bad in ward. If you are coming from a non-EU country write an email to the secretary of the hospital with a request to send an invitation for a visa. Please note that the invitation should come from the chief doctor, but not from the hospital's international department. After that you should on your own get a visa for medical treatment abroad, agree with the secretary of the chief physician on the date of the initial examination (hospitalization), translate medical records of local physicians into German or English (depending on the chosen country for treatment), book a hotel, prepare a transfer from the airport and find for yourself an interpreter for communication with the medical staff.
All these activities are not needed in case you are booking with us and you are choosing a hospital we would recommend. If you book with us, we will deal with your visa (if you are coming from a non-EU country), we will book you a hotel, and do all that is necessary to get you started with your treatment.
Shall I pay for a consultation?
A consultation before the treatment as well as long-distance consultation (if you are not from EU countries) is provided free except when you are returning to your home address and it is necessary to study CT or MRI images as the specialist gives an official consultation with a written opinion.
If you are not from EU countries it Is imperative to translate epicurises and medical records from domestic doctors into English.
If you opt for our services for the organization of treatment with us, there is no need to translate the medical records. This will be done by qualified specialists.
What happens, if I refuse from the treatment?
If you refuse from the treatment you will get a refund of the advance payment.
The expenses for all what has been done to that moment will be deducted acordingly.
Is it possible to postpone the treatment?
Yes, it is. In case of an advance postponement (more than 48 hours before the start of the treatment), the treatment cost will not be changed, and will be deleyed till as per your request. If you intend to postpone the treatment, you must do so on written only. There may be some additional cost for consultation or pre-treatment appointment, depend on the lenght from the initial day of treatment till the day you want to be.
What security and guarantees do I have?
When booking the treatment with us all medical treatment are fully insured against possible complications and unforeseen contingencies. The additional treatment costs will be covered by the insurance covered and paid by The Zdenko Kos Foundation.